Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) treatment is a type of psychotherapy or talk therapy that utilizes a cognitive-behavioral approach. Dialectical thinking refers to the ability to see that two competing or opposing forces can apply to the same thing. The dialectic at the heart of DBT is acceptance and change; in other words, I can accept myself as a worthy person even though there are some key things I need to change in order to be a healthier person.
The theory behind the approach is that some people are prone to overreact in severe and extreme manner toward certain emotional situations, creating problems with romantic, family and friend relationships. DBT theory suggests that some people get very emotionally aroused, very quickly and take a long time to return to a calm state of mind.
People who experience extreme swings in their emotions, see the world in black-and-white, and seem to always be jumping from one crisis to another typically alienate other people and create negative relationship patterns. The people that experience these outbursts usually don’t have any methods for coping with these sudden, intense surges of emotion. DBT is a method for teaching skills that will help in reducing the quick and intense responses and learn to de-escalate and self-regulate better.
DBT is also a therapy method that validates the positive aspects of a person in treatment, rather than just focusing on the negative things that they are wanting to change. It helps a person identify their strengths and builds on them so that the person can feel better about themselves and their life.
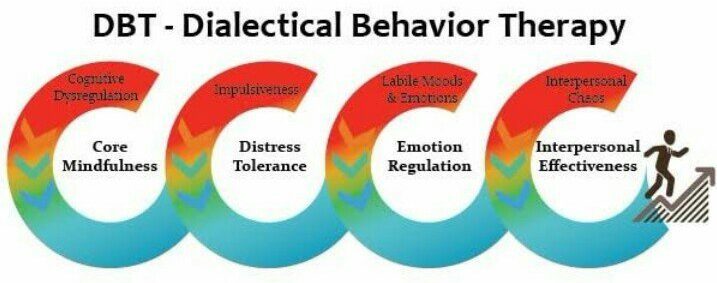
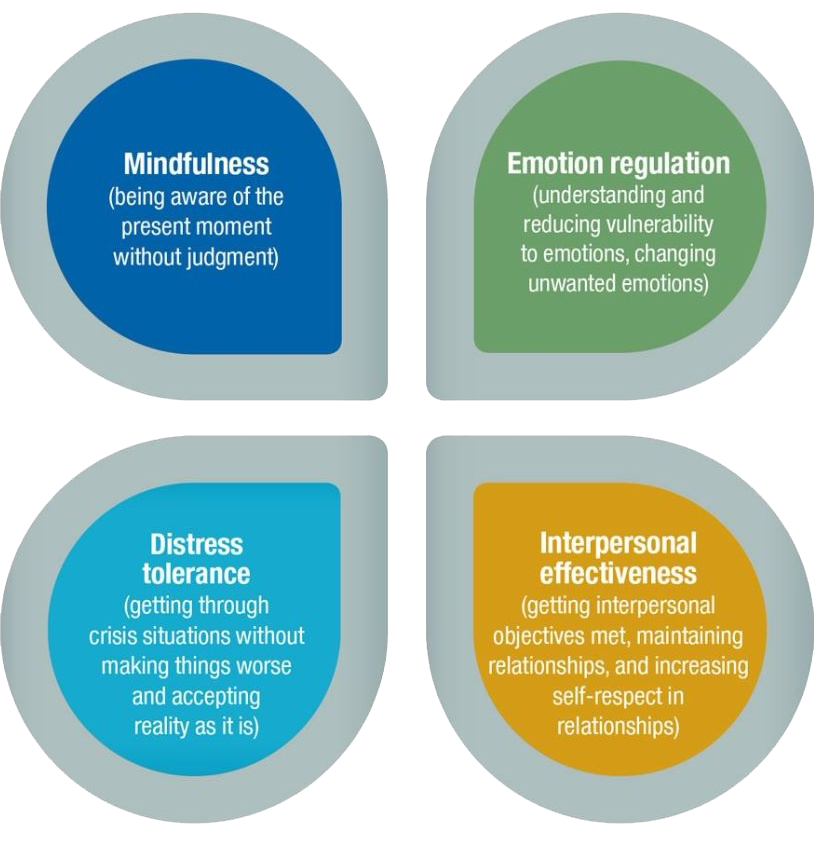
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) provides clients with new skills to manage painful emotions and decrease conflict in relationships. DBT specifically focuses on providing therapeutic skills in four key areas. First, mindfulness focuses on improving an individual’s ability to accept and be present in the current moment. Second, emotion regulation covers strategies to manage and change intense emotions that are causing problems in a person’s life. Third, distress tolerance is geared toward increasing a person’s tolerance of negative emotion, rather than trying to escape from it. Fourth, interpersonal effectiveness consists of techniques that allow a person to interact with others in a way that is maintains self-respect and strengthens relationships.